Mortgage Loan vs Home Loan – Understanding the Key Differences

When a borrower seeks financial assistance from a bank to buy or build a home, it is called a home loan. Home loans can also be used for purposes like purchasing land or renovating an existing property. The loan is repaid through equated monthly installments (EMIs), and the typical repayment period for a home loan can extend up to 30 years.
On the other hand, a mortgage loan is a type of loan taken against a property already owned by the borrower. The borrower uses their property as collateral, and the loan amount can be used for various personal or business needs. Mortgage loans typically have a shorter repayment tenure, usually up to 15 years.
Understanding the differences between a home loan and a mortgage loan is crucial for making an informed decision. Let’s dive deeper into each type of loan to help clarify these distinctions.
Home Loan vs Mortgage Loan: What’s the Difference?

If your primary goal is to purchase or build a new home, then a home loan is your best option. Conversely, if you already own property and need funds for a personal or business purpose, a mortgage loan would be more suitable. Knowing the differences between the two will help you determine which loan is best aligned with your needs and financial circumstances.
Mortgage Loans
A mortgage loan is a secured loan, meaning that the borrower pledges their property as collateral. The lender has the right to seize the property if the borrower defaults on the loan. Mortgage loans typically come with a tenure of up to 15 years.
Types of Mortgage Loans
Mortgage loans are categorized based on the way the property is used as collateral:
• Simple Mortgage: The borrower pledges their property without transferring ownership to the lender. The lender can sell the property in case of a default.
• English Mortgage: The property is transferred to the lender until the loan is repaid in full.
• Mortgage by Title Deed Deposit: The borrower deposits the title deed of the property with the lender as security for the loan.
• Mortgage by Conditional Sale: The borrower sells the property to the lender with conditions that apply if the loan is not repaid.
• Commercial Mortgage: This type is used by businesses or entrepreneurs to buy commercial properties such as office spaces or retail locations.
Benefits of Mortgage Loans

• Flexibility in Purpose: Borrowers can use the loan for any purpose, such as weddings, medical emergencies, or education.
• Large Loan Amount: The loan amount can be substantial, depending on the value of the property being mortgaged.
• Quick Access to Funds: If you already own real estate, a mortgage loan can provide immediate liquidity for urgent financial needs.
Drawbacks of Mortgage Loans
• Higher Interest Rates: Mortgage loans usually carry higher interest rates compared to home loans.
• Lower Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio: The loan amount is generally lower in relation to the property’s market value, often around 60-70%.
• Risk of Foreclosure: Failure to repay a mortgage loan could lead to the foreclosure of the property.
Eligibility Criteria for Mortgage Loans

To qualify for a mortgage loan, you generally need to meet certain criteria:
• A good credit score.
• A stable income source.
• Clear ownership documents for the property being mortgaged.
The Mortgage Loan Application Process
1. Pre-Approval: The lender assesses the borrower’s credit score, income, and the value of the property.
2. Lender Finalization: The borrower reviews quotes from different lenders and selects the one with the most favorable terms.
3. Loan Application: The borrower submits the application, including personal financial details and property documents.
4. Loan Processing: The lender evaluates the application and requests additional documentation if needed.
5. Underwriting: The lender assesses the borrower’s creditworthiness and the property’s value.
6. Closing: The borrower signs the loan agreement, pays processing fees, and the loan is disbursed.
Home Loans

A home loan is a type of secured loan used specifically for purchasing, constructing, or renovating a home. The property being purchased or constructed acts as collateral for the loan. If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender can seize the property to recover the loan amount. Home loans typically offer a higher Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio, which can be up to 90% of the property’s value.
Types of Home Loans
Home loans are available in several categories, depending on the borrower’s specific needs:
• Home Construction Loan: For borrowers who have land and need financing to build a house.
• Home Improvement Loan: For financing renovations, repairs, or upgrades to an existing home.
• Home Extension Loan: For borrowers looking to add more space to their current home, such as an additional floor or room.
• Composite Home Loan: A combination loan that finances both the purchase of land and construction of the home.
Benefits of Taking a Home Loan
• Tax Benefits: Home loan borrowers are eligible for tax deductions under sections 80C, 24, 80EE, and 80EEA.
• Lower Interest Rates: The interest rates on home loans are generally lower than those on mortgage loans.
• Long Repayment Tenure: Home loans offer longer repayment terms, typically up to 30 years, which can reduce monthly EMI burden.
• Top-Up Facility: Existing home loan borrowers may be eligible for a top-up loan at favorable rates.
Eligibility Criteria for Home Loans
To qualify for a home loan, borrowers generally need to meet the following criteria:
• A credit score of 750 or higher.
• A stable employment history and income.
• Clear ownership of the property or land.
• Adequate collateral security.
The Home Loan Application Process

1. Application: Borrowers apply for a home loan at a bank or financial institution.
2. Document Submission: The borrower submits necessary documents like proof of income, property details, and credit score.
3. Loan Evaluation: The lender evaluates the borrower’s creditworthiness and property value.
4. Approval: After the evaluation, the loan is either approved or rejected.
5. Disbursement: Once approved, the loan amount is disbursed, and the borrower can use it for purchasing or building their home.
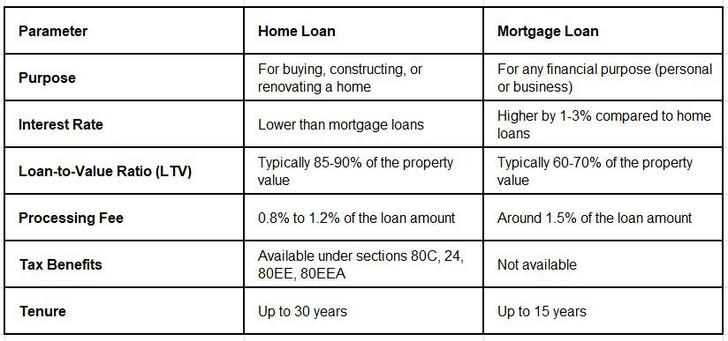
Key Differences Between Mortgage Loans and Home Loans
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between a Home Loan and a Mortgage Loan
1. Loan Purpose: Choose a home loan if you are looking to buy or build a home. Opt for a mortgage loan if you need money for other personal or business purposes.
2. Loan Amount and Tenure: Home loans generally offer a higher loan amount and longer repayment period, making them more suitable for homebuyers. Mortgage loans, while offering flexibility in usage, come with a shorter repayment period and higher interest rates.
3. Interest Rate: Home loans generally have lower interest rates, making them a more affordable option for long-term financing.
Final Thoughts
Both home loans and mortgage loans are secured loans, but they serve different purposes and come with distinct benefits and drawbacks. Home loans are ideal for purchasing, constructing, or renovating property, whereas mortgage loans can be used for a variety of personal or business needs. Understanding the nuances between these loan types will help you make an informed decision based on your financial needs and goals.
